cunqa.qpu
Contains the description of the QPU class.
These QPU objects are the python representation of the virtual QPUs deployed.
Each one has its QClient object that communicates with the server of the corresponding virtual QPU.
Through these objects we are able to send circuits and recieve results from simulations.
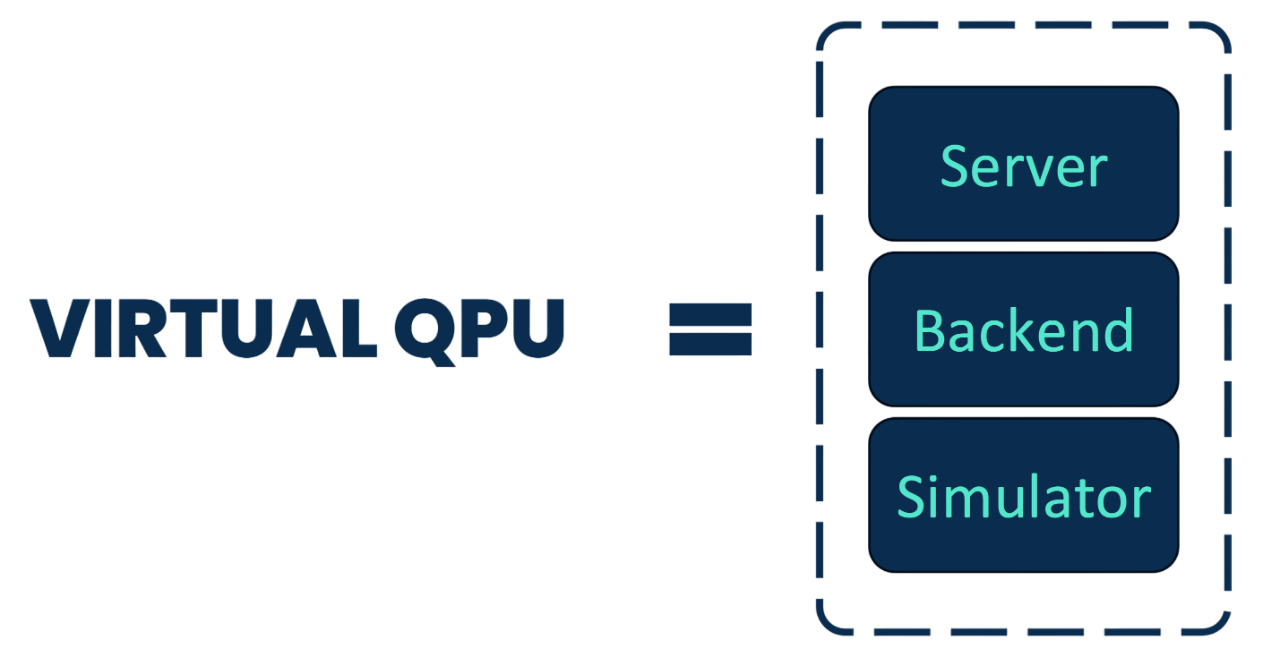
Virtual QPUs
Each virtual QPU is described by three elements:
Server: classical resources intended to communicate with the python API to recieve circuits or quantum tasks and to send results of the simulations.
Backend: characteristics that define the QPU that is emulated: coupling map, basis gates, noise model, etc.
Simulator: classical resources intended to simulate circuits accordingly to the backend characteristics.
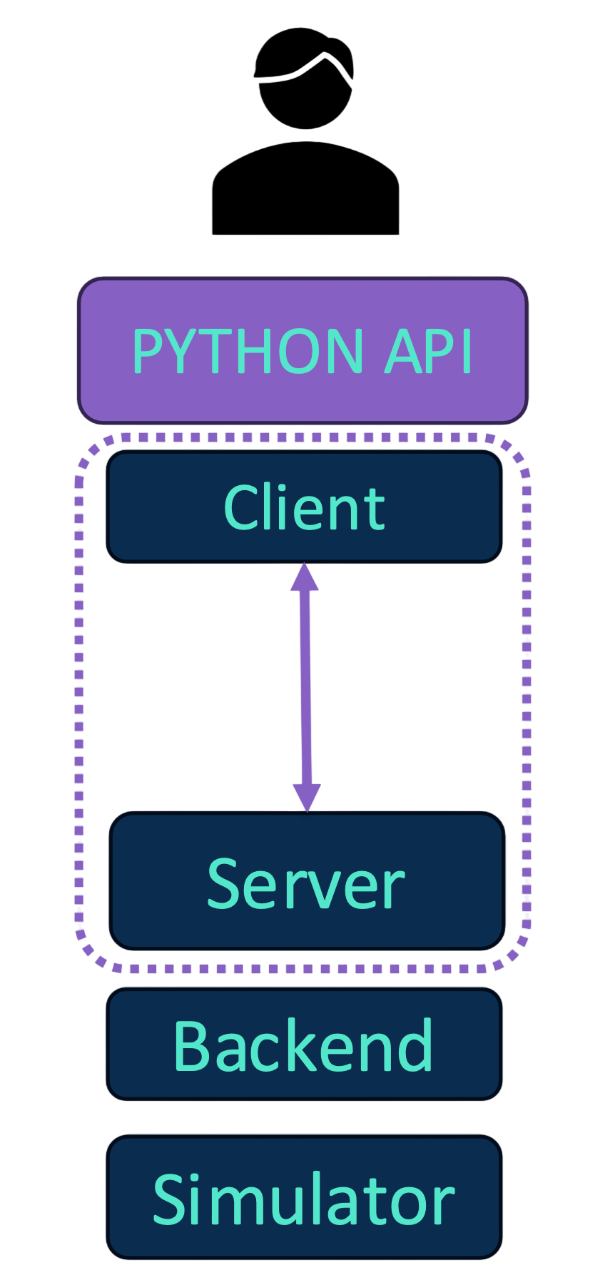
In order to stablish communication with the server, in the python API QPU objects are created, each one of them associated with a virtual QPU.
Each object will have a QClient C++ object through which the communication with the classical resoruces is performed.
Connecting to virtual QPUs
The submodule qutils gathers functions for obtaining information about the virtual QPUs available;
among them, the get_QPUs() function returns a list of QPU objects with the desired filtering:
>>> from cunqa import get_QPUs
>>> get_QPUs()
[<cunqa.qpu.QPU object at XXXX>, <cunqa.qpu.QPU object at XXXX>, <cunqa.qpu.QPU object at XXXX>]
When each QPU is instanciated, the corresponding QClient is created.
Nevertheless, it is not until the first job is submited that the client actually connects to the correspoding server.
Other properties and information gathered in the QPU class are shown on its documentation.
Interacting with virtual QPUs
Once we have the QPU objects created, we can start interacting with them.
The most important method of the class is QPU.run(), which allows to send a circuit to the virtual QPU for its simulation,
returning a QJob object associated to the quantum task:
>>> qpus = get_QPUs()
>>> qpu = qpus[0]
>>> qpu.run(circuit)
<cunqa.qjob.QJob object at XXXX>
This method takes several arguments for specifications of the simulation such as shots or transpilation. For a larger description of its functionalities checkout its documentation.
Classes
Class to represent a virtual QPU deployed for user interaction. |